An Analysis of Public Topics and Sentiments Based on Social Media During the COVID-19 Omicron Variant Outbreak in Shanghai 2022
基于社交媒体的公共话题与情感分析:以2022年上海新冠奥密克戎变异毒株疫情爆发为例
Keywords
Public health events, Concern hotpot, Sentiment analysis, Opinion governance
公共卫生事件,关注热点,情感分析,舆情治理
Highlights
• A research framework was constructed to analyze public themes and sentiments based on 90,000 Weibo data entries.
• 基于90,000 条微博数据,构建了分析公共主题和情感的研究框架。
• 采用 LDA 主题模型和 SnowNLP 情感分类方法,量化了公众情感值。 • Spatiotemporal visualization revealed the evolution of public concerns and sentiment trends.
• 通过时空可视化,揭示了公众关注点和情感趋势的演变特征。 • The study found that changes in public sentiment were primarily influenced by the severity of the pandemic, sudden incidents, resource availability, and government responsiveness.
• 研究发现,公众情感的变化主要受到疫情严重程度、突发事件、资源供应及政府响应能力的影响。
Introduction
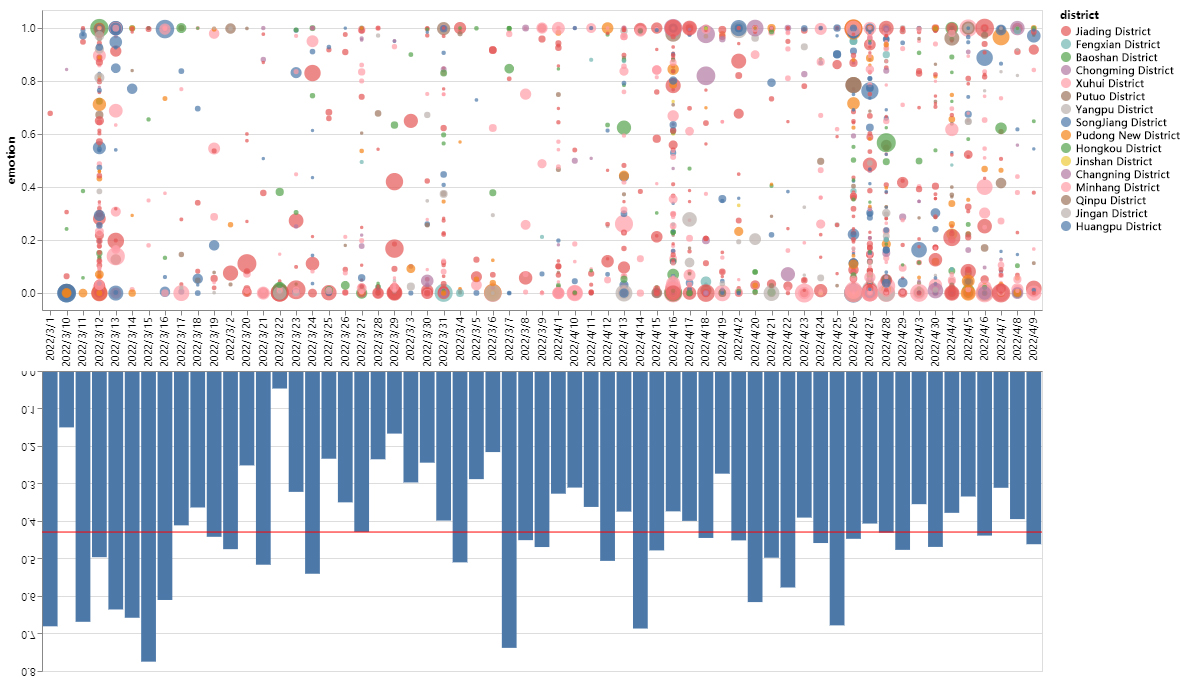
The outbreak of the COVID-19 Omicron variant in Shanghai in 2022 elicited complex emotions among Shanghainese during the two-month quarantine period. This paper aims to identify prevailing public themes and sentiments by analyzing social media posts from Weibo. Initially, we conducted research based on a dataset of 90,000 Weibo posts during the 2022 COVID-19 outbreak in Shanghai. By examining social media data that mirrors residents' emotional shifts and areas of focus during unforeseen circumstances, we have developed an analytical framework combining hotspot analysis and public sentiment assessment.
2022年新冠疫情奥密克戎变异毒株在上海暴发,在为期两个月的封控期间,上海市民产生了复杂的情绪。本文旨在通过分析微博上的社交媒体帖子,来识别大众普遍关注的主题及情绪。首先,我们基于 2022 年上海新冠疫情期间 9 万条微博帖子的数据集开展了研究。通过审视这些反映居民在突发情况下情绪变化及关注重点的社交媒体数据,我们构建了一个将热点分析与公众情绪评估相结合的分析框架。
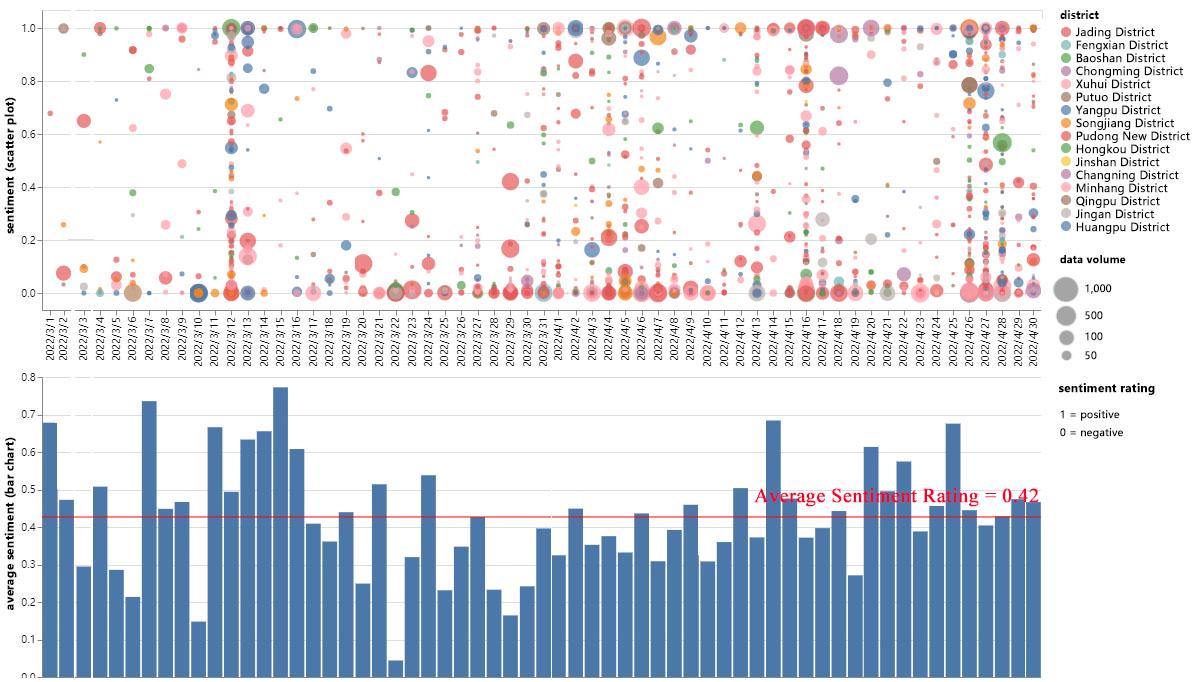
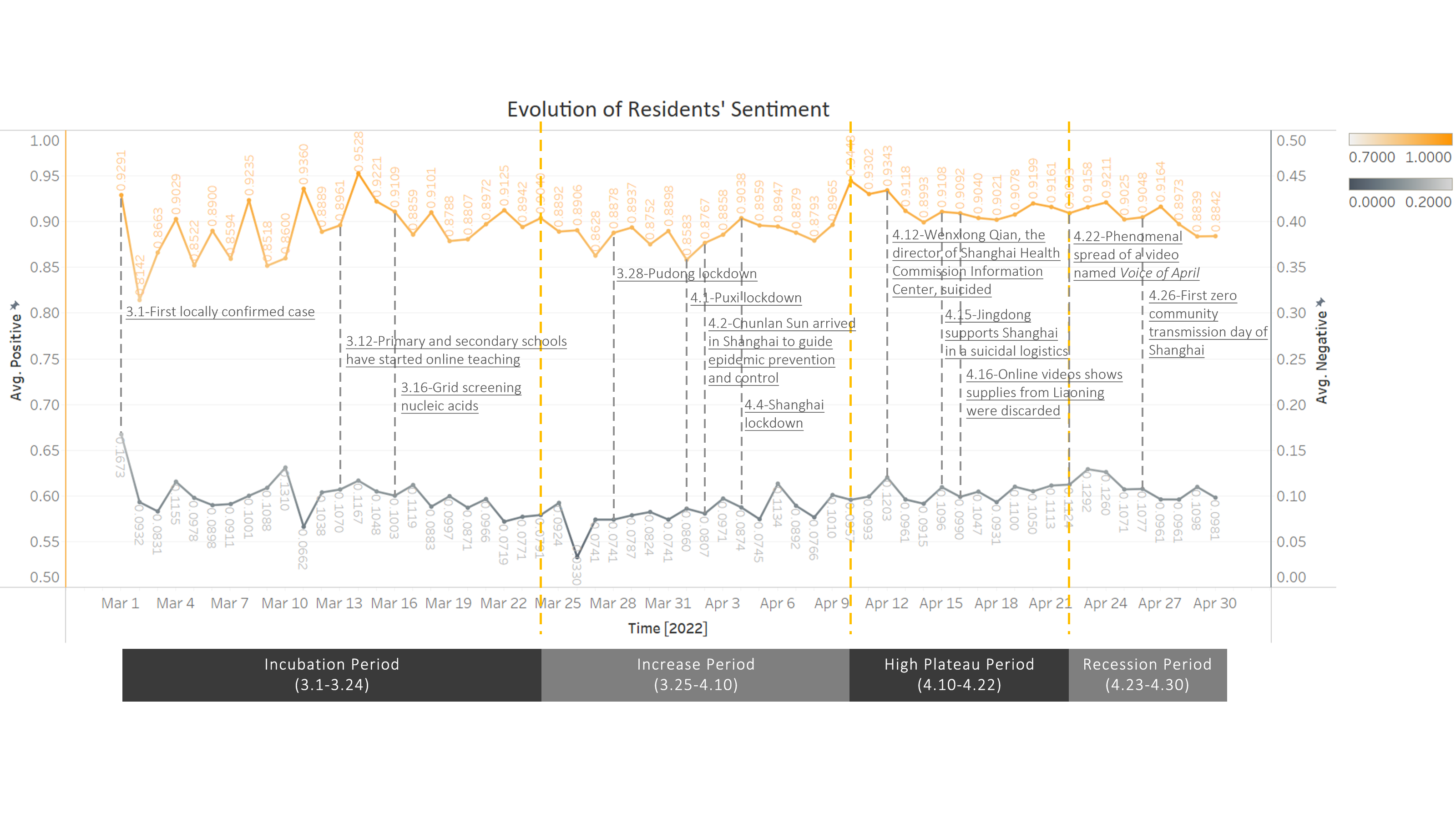
Subsequently, we employed the Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) method to conduct topic modeling on the Weibo text data. The SnowNLP sentiment classification method was then utilized to quantify sentiment values. Ultimately, we performed spatial visualization of sentiment and concern data, categorizing them into distinct time periods based on Shanghai's infection curve. This approach allowed us to investigate concern focal points, sentiment trends, and their spatiotemporal evolution characteristics.
随后,我们运用潜在狄利克雷分配(LDA)方法对微博文本数据进行主题建模。接着采用 SnowNLP 情感分类方法对情感值进行量化。最终,我们对情绪及关注数据进行了空间可视化处理,并依据上海的感染曲线将其划分到不同时间段。这种方式使我们能够探究关注焦点、情绪趋势及其时空演变特征。
Our findings indicate that variations in public sentiment primarily hinge on the severity of the epidemic's spread, emerging events, the availability of essential resources, and the government's ability to respond promptly and accurately. It is evident that, while residents' concerns shift over time, their primary objective on social media remains expressing demands and releasing emotions. This research offers an avenue for leveraging public opinion analysis to enhance governance capacity during crises, fortify urban resilience, and promote public involvement in governmental decision-making processes.
我们的研究结果表明,公众情绪的变化主要取决于疫情传播的严重程度、突发事件、基本资源的可获取性以及政府能否及时且准确地做出应对。显然,尽管居民的关注点会随时间变化,但他们在社交媒体上的主要目的依然是表达诉求和宣泄情绪。这项研究为利用民意分析来提升危机期间的治理能力、增强城市韧性以及促进公众参与政府决策过程提供了一种途径。
Publication
Liu, C., Tian, Y., Shi, Y. et al. (2024).
An analysis of public topics and sentiments based on social media during the COVID-19 Omicron Variant outbreak in Shanghai 2022.
Computational Urban Science.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s43762-024-00128-y
materials
Data utilized in this research are public information.
Our computer codes are available upon request.