The impacts of the built environment on the incidence rate of COVID-19: A case study of King County, Washington
建成环境对新冠肺炎发病率的影响:以华盛顿州金县为例
Keywords
Sustainability, Urban density, Socioeconomic factors, Air quality, MLR, Urban planning, Built environment, Post COVID-19 pandemic
可持续性,城市密度,社会经济因素,空气质量,多元线性回归(MLR),城市规划,建成环境,后新冠疫情时代
Highlights
• Focus on the impacts of built environment on incidence rate of COVID-19 in metropolitan area.
• 聚焦建成环境对大都市地区COVID-19发病率的影响。
• 在邮政编码尺度上建立了多元线性回归和地理加权回归模型。 • Socioeconomic indicators are the primary factors influencing COVID-19.
• 社会经济指标是影响COVID-19的主要因素。 • Built environment density is positively associated with incidence rates.
• 建成环境密度与发病率呈正相关。 • Increased open space is conducive to reducing incidence rates and overcrowded households leads to an increase in incidence rates.
• 增加开放空间有助于降低发病率,而过度拥挤的家庭会导致发病率上升。
Introduction
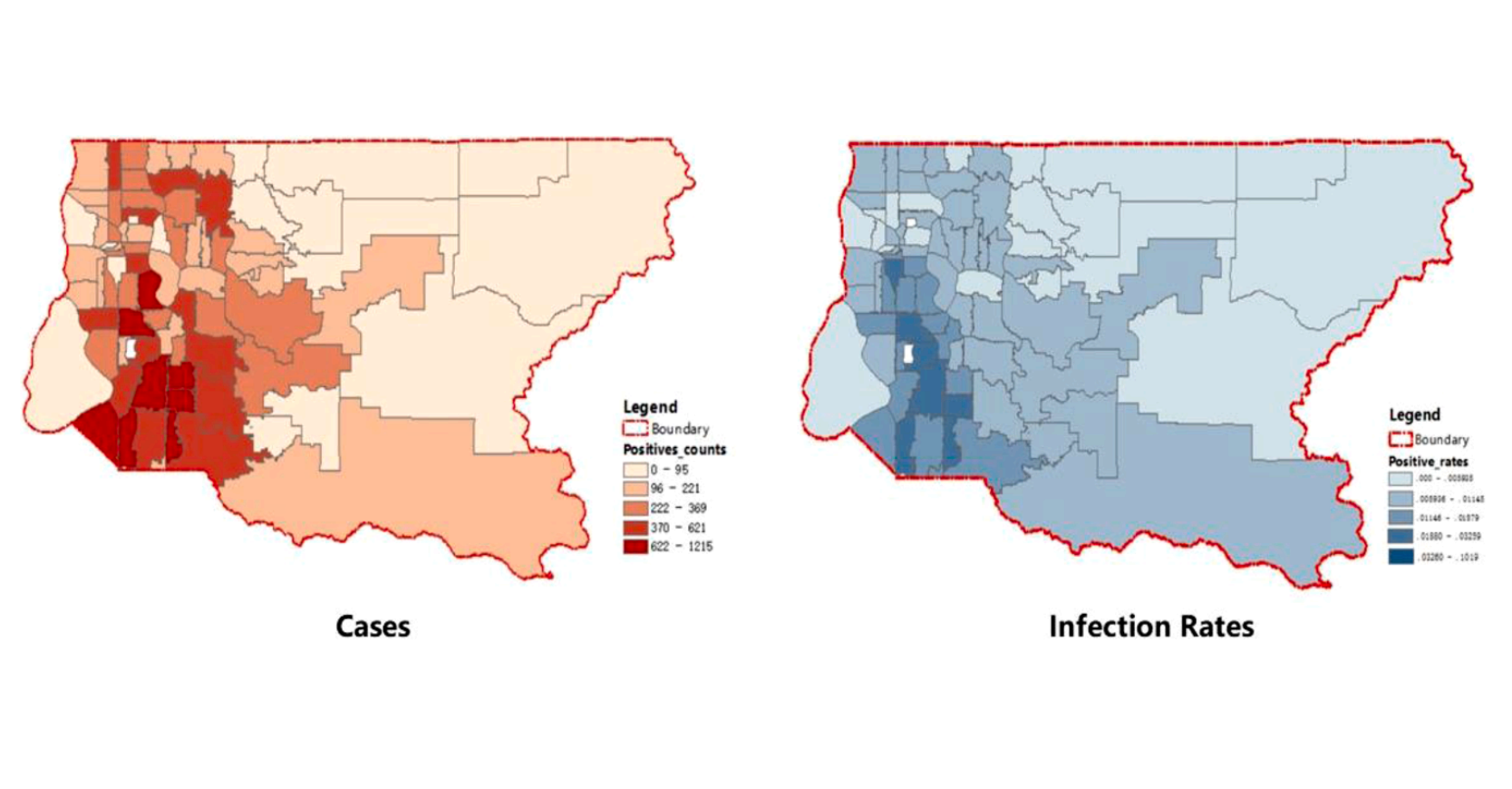
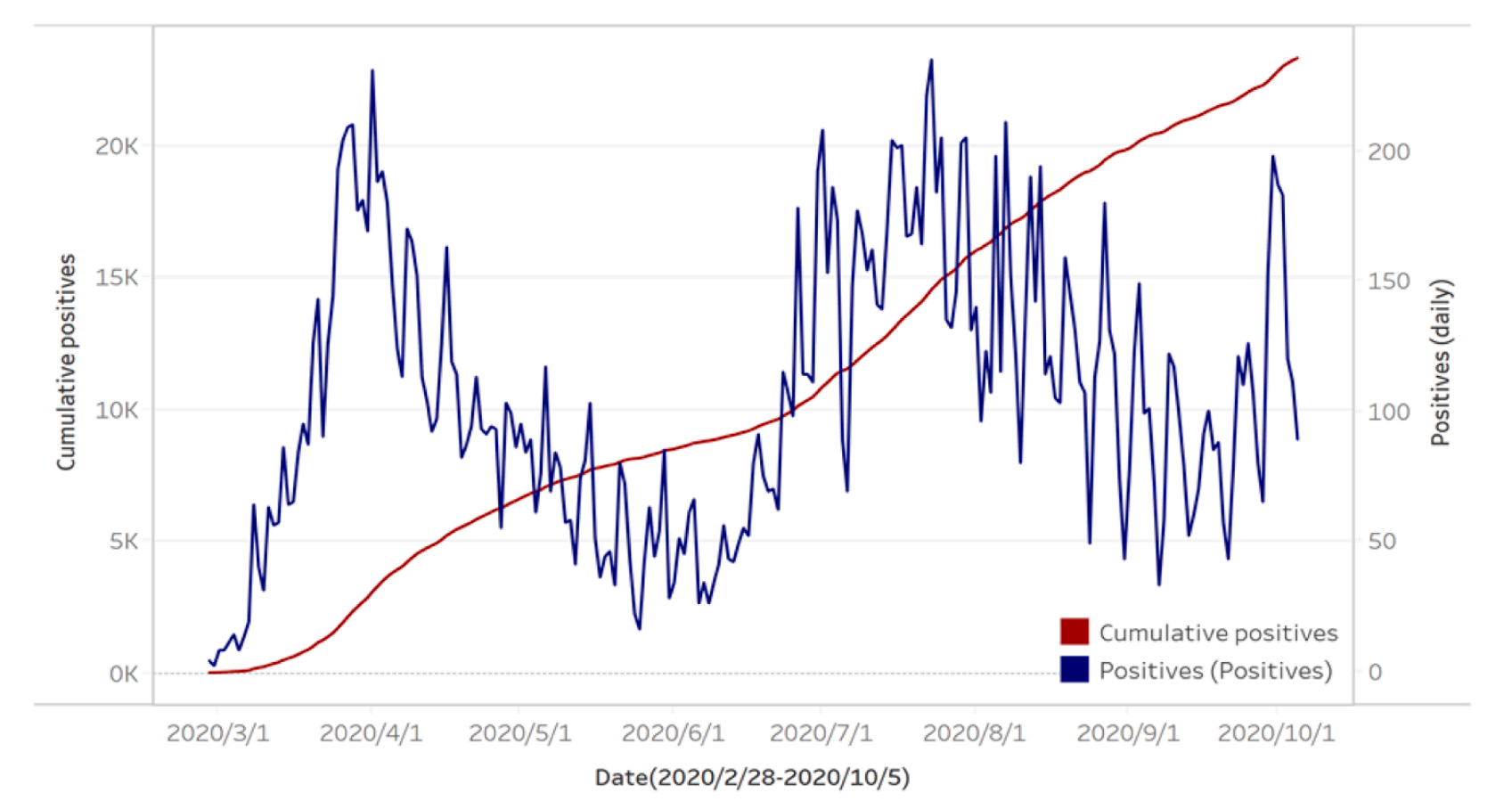
This study examines how the built environment influences the incidence of COVID-19, focusing on King County, Washington. By leveraging spatial analysis and statistical models, the research highlights the interplay between urban density, socioeconomic factors, and land use on infection rates. The findings provide actionable insights for sustainable urban planning and public health interventions, emphasizing the importance of open spaces, equitable housing, and strategic density management in combating infectious diseases.
本研究探讨了建成环境如何影响华盛顿州金县的 COVID-19 传播率。通过空间分析和统计模型,研究揭示了城市密度、社会经济因素和土地利用对感染率的交互影响。研究结果为可持续的城市规划和公共卫生干预提供了实用见解,强调开放空间、公平住房和战略性密度管理在应对传染病中的重要性。
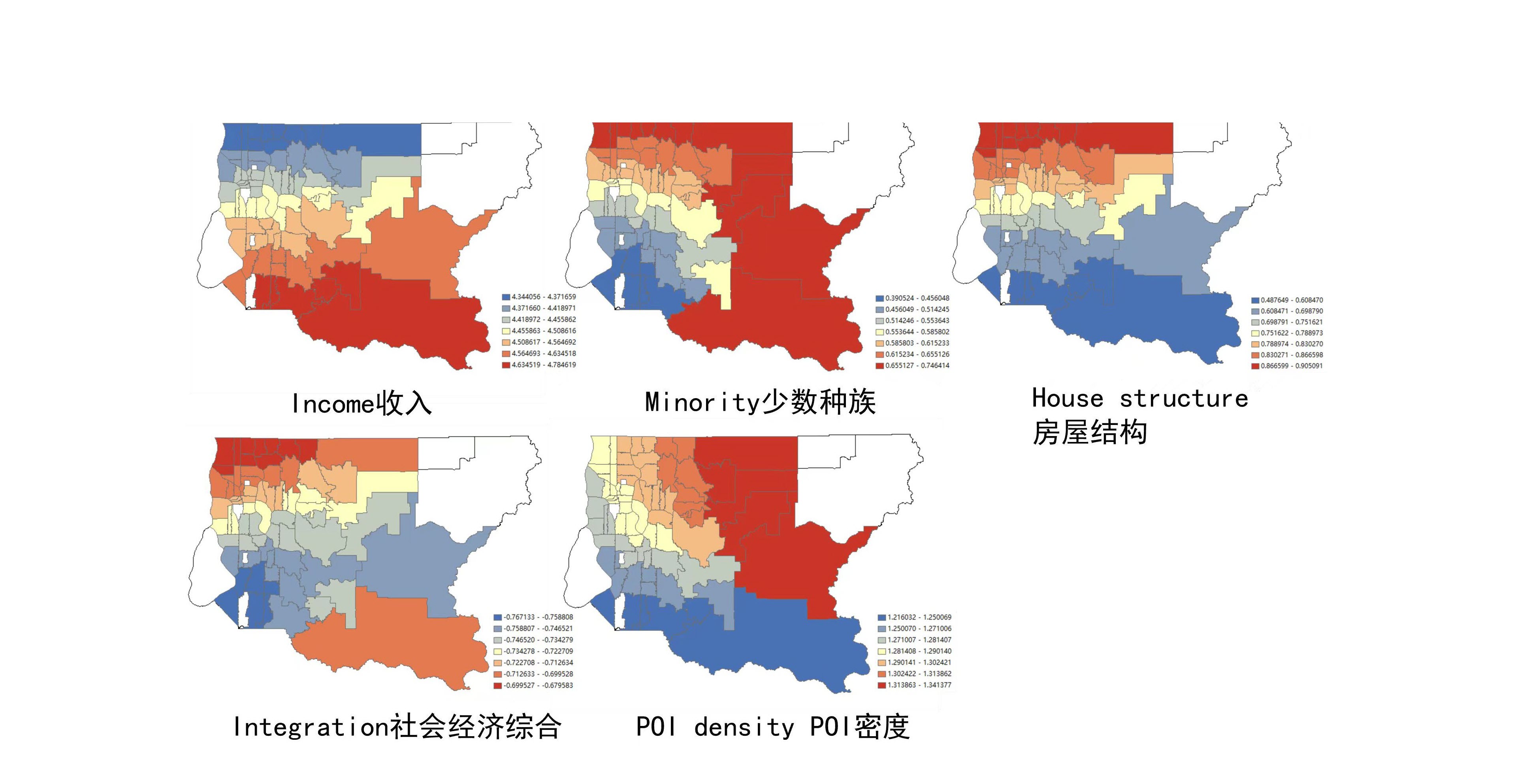
This study drew initial conclusions regarding the association between the built environment and the transmission of infection in the typically metropolitan area of King County, Washington. Integrating socioeconomic and meteorological factors, we focused on attributes related to the built environment, notably land use, POI distribution, population density, building concentration, road networks and households. Conducting PCA-MLR, PCC-MLR and GWR models, we explored methods that could be used to study infectious diseases in urban areas.
这项研究初步得出了关于建筑环境与感染传播之间关系的结论,研究对象为典型的都市区——华盛顿州金县。通过整合社会经济和气象因素,我们重点关注了与建筑环境相关的属性,尤其是土地利用、POI分布、人口密度、建筑集中度、道路网络和家庭分布。通过进行主成分分析-多元线性回归(PCA-MLR)、皮尔逊相关系数-多元线性回归(PCC-MLR)和地理加权回归(GWR)模型分析,我们探索了可以用来研究城市地区传染病的多种方法。
The main novel contributions of this paper are as follow: firstly, this study is among the first to consider spatial factors (notably building density, road networks, POI distribution, and land use intensity) in urban areas at the county level, filling a research gap in the built environment. Secondly, we built different models to describe the temporal and spatial distributions of the results. Finally, the analysis results may effectively guide sustainable development in cities, making the built environment more suited to human settlement.
本文的主要创新贡献如下:首先,本研究是首批考虑县级城市地区空间因素(特别是建筑密度、道路网络、POI分布和土地利用强度)的研究之一,填补了建筑环境领域的研究空白。其次,我们建立了不同的模型,以描述结果的时间和空间分布。最后,分析结果可能有效地指导城市的可持续发展,使建筑环境更加适宜人类居住。
Publication
Chao Liu, Zerun Liu, ChengHe Guan. (2021).
The impacts of the built environment on the incidence rate of COVID-19: A case study of King County, Washington.
Sustainable Cities and Society.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2021.103144
materials
Appendix. Supplementary materials: Download Word document.